Cryptocurrencies have opened new doors in modern finance. As this digital financial frontier continues to attract individuals and organizations, the pressure to protect these virtual riches from hidden risks has increased. Crypto wallets—fortified lockers that protect your digital assets—are vital. In this detailed book, we explore crypto wallets and provide effective advice to secure your important assets. We help you comprehend public and private keys and wallet kinds to protect your crypto valuables. We’ll reveal crypto wallet security so you may confidently invest in cryptocurrencies.
I. Understanding Crypto Wallets

Cryptocurrency wallets protect and allow. Crypto wallets store, monitor, and enable digital asset transactions. It protects your digital assets like a virtual vault.
Crypto wallets use public and private keys. Your wallet may receive coins using your public key, a cryptographic address. However, the private key is like the key to your safe, allowing you to sign transactions and access your assets.No banks or middlemen manage Bitcoin transactions. Instead, a blockchain—a decentralized, unchangeable ledger—validates and records them. Your wallet uses your private key to sign transactions, proving ownership and authorization. Understand that different crypto wallets suit different tastes and security demands. These include hardware wallets, software wallets, and paper wallets. By knowing crypto wallets and their crucial function in safeguarding and maintaining your digital assets, you may confidently enter the cryptocurrency world and gain financial independence.
II. The Importance of Securing Your Crypto Assets
Digital finance requires crypto asset security. Cryptocurrencies’ rising popularity has drawn both legal investors and criminals. Hacking attempts and exchange vulnerabilities abound. Cryptocurrencies are decentralized, pseudonymous, and need individual security.
- Growing Threat Landscape
Hackers and phishers now target both beginners and experts in crypto. Crypto exchanges have also been breached, resulting in significant losses. Security breaches are serious because bitcoins are decentralized and hard to recover.
- Regulatory Factors
Owners must secure crypto assets without central control. Lost or stolen bitcoins have complicated legal consequences that differ by country. Businesses and individuals must traverse this complex landscape, knowing that security breaches can have serious implications.
III. Types of Crypto Wallets
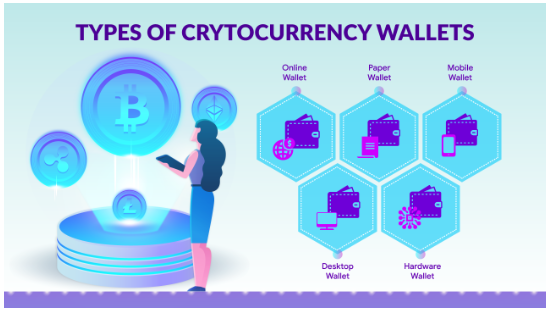
There are several wallet alternatives for cryptocurrency security. Each kind has pros and cons, allowing users to adjust security to their risk tolerance and usage habits.
- Hardware wallets
Hardware wallets protect crypto. These USB-like gadgets secure your secret keys offline. Hardware wallets are appropriate for long-term asset preservation due to their internet isolation, which reduces hacking and phishing risks.
- Software wallets
Desktop, mobile, and web software wallets exist. They’re useful for frequent transactions but riskier than hardware wallets because they run online. Mobile wallets are portable, whereas desktop wallets store keys locally for security. Online wallets are more vulnerable to hacks, thus security is crucial.
- Paper wallets
Cold storage paper wallets generate and print keys. They need physical security despite being offline and cyber-secure. Paper wallets are suitable for long-term, infrequent asset access.
IV. Best Practices for Crypto Wallet Security

Protecting crypto assets requires proactive security measures. These recommended practices strengthen digital asset security and reduce risk.
- Strong passwords and 2FA
Use mixed-character wallet passwords. Two-factor authentication (2FA) prevents unauthorized access wherever feasible.
- Software Updates
Update your wallet software often for security and bug updates. Hackers may exploit flaws in outdated software, endangering your valuables.
- Backup/Recovery
Encrypt wallet and private key backups. To recover from loss, theft, or hardware failure, store backups off-site.
- Physical Security
Protect hardware wallets like valuables. Safely store paper wallets in waterproof, fireproof containers.
V. Mistakes to Avoid

Cryptocurrency offers unmatched prospects but also risks. Protecting crypto assets requires knowing and avoiding common pitfalls.
- Untrusted Wallets and Exchanges
- Not researching wallet providers and exchanges might put your funds at risk. Choose trusted choices to reduce hazards.
- Use official sources to protect your assets.
- Avoiding Security Updates
Delaying wallet software upgrades leaves you vulnerable. Updating regularly protects your wallet.
- Sharing Private Data
- Exposure of your private key allows unauthorized access to your cash. Always protect your private key.
- Never reveal wallet addresses or transaction data. Cybercriminals may target such information.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies are changing fast, thus secure crypto wallets are essential. Strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and frequent updates protect against attackers. Secure backup and recovery practices keep assets accessible in crises. Physical security is essential for hardware, software, or paper wallets. Maintaining control and peace of mind in this turbulent world requires work. Following these recommended practices, you may confidently embrace the exciting potential of cryptocurrencies while protecting your investments.
